If you’ve ever felt a bolt of pain travel through your spine or experienced a dull, constant ache in your lower back, you’re not alone. Forty millioni Americans experience back pain. Eighty percentii of Americans will suffer from some type of back pain during their lives. Acute (sudden onset) and chronic (ongoing) back pain can affect one’s quality of life and result in major life changes, including job loss and broken relationships.
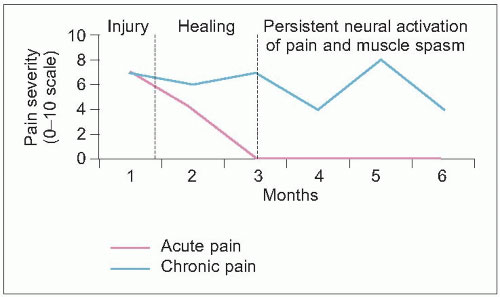 Acute pain: A short-term pain with a sudden onset is known as “acute.” You can typically identify an action or injury that caused an acute pain, such as lifting something too heavy. Pain from an acute back injury can last from several hours up to a month, but it usually resolves on its own. See your doctor to be certain it’s not serious and to receive a treatment plan.
Acute pain: A short-term pain with a sudden onset is known as “acute.” You can typically identify an action or injury that caused an acute pain, such as lifting something too heavy. Pain from an acute back injury can last from several hours up to a month, but it usually resolves on its own. See your doctor to be certain it’s not serious and to receive a treatment plan.
Subacute pain: Subacute pain is like acute pain but can last up to three months. See your doctor for a treatment plan and follow it carefully so the pain doesn’t become chronic.
Chronic pain: Pain that is chronic can last longer than three months. The cause of chronic pain might be a single incident, or it might be the result of constant, repetitive motions made by the body while at work or during sports. If left untreated, chronic pain can be debilitating and could negatively affect one’s career, relationships, and mental health.
Everyone is different. Our bodies are unique, and they can change based on our occupations, hobbies, habits and sometimes our environment. It’s easy to see how there can be many causes of back pain, including:
Back pain can be different for everyone. Symptoms that are most often reported include:
See a doctor for a proper diagnosis of your back pain. This often includes a health history, a physical exam, possibly bloodwork, and generally imaging studies such as X- rays, MRI or CT scans.
Your doctor may begin your course of back pain treatment conservatively, with anti- inflammatory medication, heat and physical therapy. If your pain fails to respond to treatment, a back specialist might administer injections to block the pain. Back surgery is typically considered later, if a more conservative treatment plan fails as a back pain remedy.
Today’s advanced surgical treatment options have proven highly successful in treating back pain. These include:
Disc replacement: An alternative to spinal fusion for some patients with degenerative disc disease; provides the possibility for motion in the affected area
Micro-Discectomy: A surgical procedure that removes a damaged disc, including any bulging components that have impinged upon nerves in the lower back or neck; typically uses smaller incisions than an open surgery
Spinal fusion: Provides security and stability to patients who are not candidates for total disc replacement
Chronic back pain used to be debilitating, but thanks to major surgical advances and treatment options, that doesn’t have to be the case. Therefore:
Consider all your lower back pain treatment options.
These individuals can inspire your journey to healing and life after disc replacement surgery—and the hope of freedom from spine-induced pain and discomfort.
To Find a Spine Surgeon That's Right for You, Use our Surgeon Locator